User blog: Astrid Dinneen
By Hampshire EMTAS Specialist Teacher Advisors Lisa Kalim and Astrid Dinneen
In the academic year 2021-22, Hampshire EMTAS saw its highest ever increase of referrals for asylum seekers and refugees with over 300 referrals made by schools. The majority were for children and young people from Afghanistan and Ukraine. The former was caused by the Taliban reclaiming power in Afghanistan in summer 2021 and the latter by the war in Ukraine starting in spring 2022.
In order to better support these children and families, Hampshire EMTAS welcomed new Bilingual Assistants on to the team covering Pashto, Dari, Farsi and Ukrainian languages. The Teacher Team caught up with these new colleagues to find out more about the backgrounds of these children. This highlighted many areas which school practitioners will find useful when settling and supporting their new arrivals. Lisa Kalim and Astrid Dinneen summarise these key areas before concluding with a list of recommendations and further resources.
Climate
In general, Afghanistan has extremely cold winters and hot summers, although there are regional variations. Most of the precipitation falls between December and April, with the summer months being very dry apart from in the south-eastern region. Afghan children may not consider our winters to be particularly cold or our summers particularly hot and may for example not feel the need to wear a coat in winter or short sleeves in summer.
In contrast, Ukraine has a temperate climate, with winters in the west being considerably milder than in the east. In summer, the east often has higher temperatures than the west. Summers are much wetter than winters with June and July being the wettest months. The west of Ukraine tends to have more rainfall than the east.
Geography
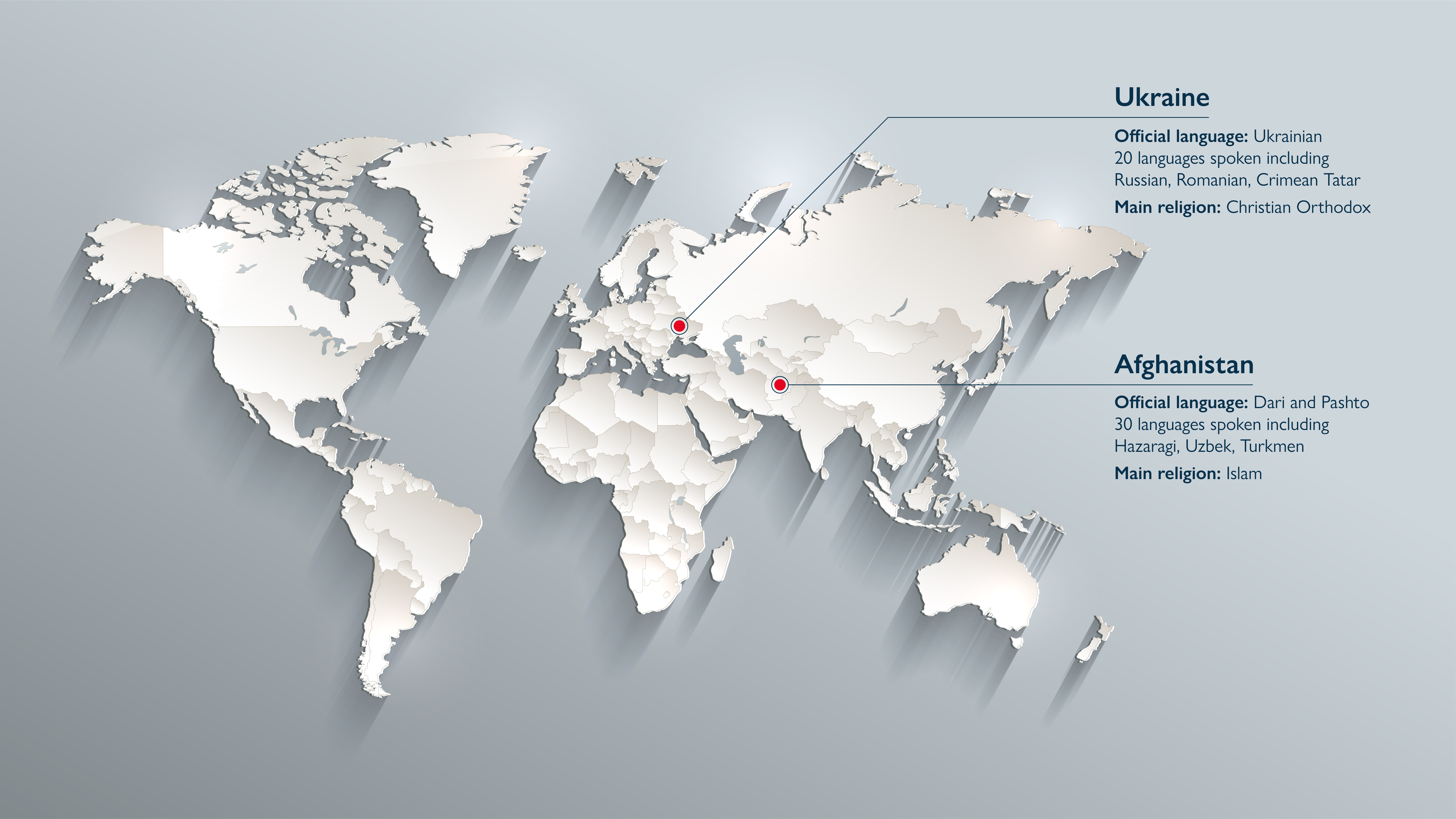
Afghanistan is a landlocked country in south-central Asia. It borders Pakistan to the east and south, Iran to the west, and the states of Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Tajikistan to the north. It also has a short border with China in the extreme north-east. It covers an area more than twice the size of the UK. Afghanistan is divided into 34 provinces, each of which is sub-divided into 421 districts for administrative purposes. There are extensive mountainous areas, as well as high plateaus and plains. Mountains cover about three-quarters of the land area, with deserts in the south-west and north. The people of Afghanistan mainly live in rural areas in the fertile river valleys between the mountains, although the desert areas of the southwest are also becoming more populated. About 4.5 million people live in the capital, Kabul, in the east of the country.
Ukraine is located in eastern Europe and has borders with Belarus to the north, Russia to the east, Moldova and Romania to the south-west and Hungary, Slovakia and Poland to the west. In the south it has over 1,700 miles of coastline along the Sea of Azov and the Black Sea. It also covers an area more than twice the size of the UK but is slightly smaller than Afghanistan. Ukraine is a largely flat, relatively low-lying country consisting of plains with mountainous areas only in small areas near its southern and western borders. The majority of people live in urban areas in Ukraine with rural areas being much less densely populated. The east and west of the country have urban areas with higher populations, together with the cities of Kyiv in the north and Odessa in the south.
Languages
More than 30 languages are spoken in Afghanistan. Many Afghans are bilingual or multilingual. There are two official languages, Dari (also known as Farsi or Persian) and Pashto. Dari is more widely spoken than Pashto, with over 70% of the population speaking it either as a first or second language. It can be heard mainly in the central, northern, and western regions of the country. It is considered to be the language of trade, it is used by the government, its administration and mass media outlets. However, it is estimated that less than 50% of Dari speakers are literate. The primary ethnic groups that speak Dari as a first language include Tajiks, Hazaras, and Aymaqs.
Around 40% of the population are first language Pashto speakers, with a further 28% speaking it as an additional language. It can be heard predominantly in urban areas located in the south, southwest, and eastern parts of the country. Pashto is used for oral traditions such as storytelling as a high proportion of Pashto speakers are not literate in the language. Although spoken by people of various ethnic descents, Pashto is the native language of the Pashtuns, the majority ethnic group.
There are also five regional languages - Hazaragi, Uzbek, Turkmen, Balochi, and Pashayi. Hazaragi is a dialect of Dari. Additionally, there are around 30 other languages spoken by minority groups in Afghanistan including Pamiri, Arabic and Balochi.
There are at least 20 languages spoken in Ukraine. The most widely spoken is Ukrainian which is the country’s official language. Russian is spoken as a first language by approximately 30% of the population, mainly in the east near the border with Russia and in the south in Crimea. Generally, Russian speakers are more likely to live in cities, and are not found in large numbers in rural areas. Many first language Ukrainian speakers will also speak Russian as a second language. However, recently the Russian language has become a very sensitive issue for Ukrainians and now many Ukrainians do not want to use Russian at all. Other minority languages spoken in Ukraine include Romanian, Crimean Tatar, Bulgarian, Hungarian, Armenian, Belarusian and Romani.
School starting age
School starting age in both Afghanistan and Ukraine is much later than in the UK. Typically, Afghan children will start school at the age of 7. Many new arrivals into Hampshire will have attended school however many were not able to attend due to factors such as having to work to support their family, school being too far from their home, fears of terrorist attacks on schools, gender and of course COVID. As a result, the formal education of many children is fragmented or minimal. This can make it harder for these children to settle in school in the UK as many are not used to attending school regularly. When attending school in Afghanistan, children would attend half a day (about 3 ½ hours a day) hence attending a full school day in the UK would be very tiring for many new arrivals initially.
In Ukraine, parents will send their children to school between the age of 6 and 7. Until then, children will typically attend nursery where the curriculum is play based and where children still nap in the afternoon. This means that these children will find it hard to complete a full day in Year R and Year 1 due to tiredness as they are used to sleeping in the middle of the day. Additionally, it is common for children to go to bed much later than is usual in the UK ie between 22.00 and 23.00. This can also contribute to tiredness and settling in issues including behaviour problems. In primary school the academic part of the day usually finishes at around 1 pm and children attend clubs in the afternoon.
Attendance
In Afghanistan children may be accompanied to school by family members or neighbours in the early days of the academic year and they will usually walk to and from school without an adult for the rest of the year. Some children may choose not to attend and have a day out instead. Parents may not find out about their children missing school because absences are not routinely reported, particularly in state schools. In private schools however children have a home-school diary which supports communication between home and settings and any issues such as lateness, absences, lack of homework etc. are reported in writing.
In Ukraine, expectations around attendance are different from that in the UK. For example, children with a runny nose and a mild cough are considered by their families to be poorly hence they are kept away from settings for long periods of time eg a week or two. This tends to be encouraged by teachers in Ukraine. Similarly, parents in Ukraine will often take their children out of school to go on holiday or for an extended weekend away.
It may be necessary for school practitioners to have conversations with parents about expectations and the law around attendance in the UK and the requirement to let the school know if children are going to be absent.
School facilities
In both Afghanistan and Ukraine, facilities depend on whether schools are state or private and on whether they are located in a city or a remote village.
In Afghanistan, girls and boys are educated separately in state schools. However in private schools they are taught together. Class sizes in Afghanistan tend to be very large. Facilities in private schools may include buildings with classrooms and sometimes IT and Science equipment whereas in rural areas classes may take place outside as there may not be a building (it might not exist or may have been destroyed). State and private secondary schools are now closed for girls since the Taliban took over in Summer 2021.
In Ukraine there are also regional disparities affecting school facilities as well as differences between private and public sectors. Facilities eg interactive whiteboards may also depend on donations from families. Class sizes are similar to those in the UK.
Teaching and learning
In Afghanistan, children wear a uniform at school. Dari and Pashto are taught in both private and state schools together with Maths, Science, Geography, History and Art. English is taught from Year 4 in state schools and from Year 1 in private schools. IT is taught where facilities allow – sometimes through textbooks, sometimes through practical work. Since the Taliban came back to power there is more of a focus on religious studies than other subjects. Children in Afghanistan are usually taught from the front and are not expected to speak to each other or to work collaboratively, just copy from the board. When children deviate from this, corporal punishment is used to discipline them.
In Ukraine the range of subjects is similar to that offered in the UK. The language of instruction is Ukrainian across the whole country and most pupils, including Russian speakers, use Ukrainian for academic purposes. Russian is not taught in schools and is not part of the curriculum. Often even Russian speaking children are not literate in Russian. Younger children may know only the basics. Older children may be more confident with reading and writing in Russian however this is usually because they have taught themselves or learnt with their parents. Children do not wear a uniform. The teaching style in state schools is traditional with children being expected to sit passively and not move around the classroom. This means that new arrivals in the UK will have to adjust to a more active and collaborative approach to learning. In fact, newly arrived Ukrainian children sometimes report that they cannot distinguish the difference between lessons and break times in the UK.
In Ukraine pupils are used to receiving plenty of homework daily and families – usually mothers – tend to spend large amounts of time supporting their children with this every day. Outside of school families will commonly also employ private tutors. Families arriving in the UK have reported their surprise at how little homework their children receive in comparison. They also report not having a good grasp of how well their children are doing here because of the differences in grading work completed at school and at home. Homework is also very important in Afghanistan and children receive it daily.
In Ukraine, children would not be expected to play outside when it rains. In fact, settings should be aware that water play – even in the summer months – is not a well-accepted learning activity because the children may get wet. Similarly, sitting on the floor is not acceptable in Ukraine - particularly for girls.
In both Afghanistan and Ukraine children are required to pass assessments in order to progress to the next year group. In practice it is rare for Ukrainian children not to progress but it is relatively common in Afghanistan.
Extra-curricular activities
In Afghanistan children may attend private language centres to learn English outside of school. They may also attend taekwondo or karate clubs as well as private art courses. Some children work part-time to support their families however many families prefer to live modestly to be able to afford extra-curricular activities for their children. Football and cricket are very popular sports in Afghanistan.
Music schools are popular in Ukraine and it is usual for children to attend up to three times a week. Many children will have brought their musical instruments to the UK to continue practising. Sports such as athletics and gymnastics are also very popular and clubs are attended just as often. Children’s assiduity means their skills can surpass that of their UK peers. Settings should make every effort to find out about children’s interests and signpost ways for them to continue developing those skills in or outside of school.
SEND
Children with SEND do not usually attend school in Afghanistan, particularly in rural areas. Instead, it is likely that they would be kept at home. There is very little educational provision available in Afghanistan for children with SEND at present, but this is beginning to change. There are a few schools that specialise in children with SEND in the larger cities, but these are mostly private and so parents would need to be able to afford the fees for their children to attend. Kabul has the country’s only school for visually impaired children which is government funded and there are also schools for hearing impaired children in Kabul and Jalalabad. Additionally, there are other small schools in Kabul catering for children with a wide range of SEND, some of which do not charge fees as they are funded by charitable donations. For those children with SEND who are able to attend standard schools, no additional support is available. These children will not be able to progress to higher year groups if they fail the end of year exams and so may have to repeat a year several times. Many of these children will eventually drop out of school as a result.
In contrast with Afghanistan, children with SEND in Ukraine do usually attend school. In the past, these children were educated away from the mainstream in either special schools for those with SEND, including boarding schools, or in separate classes held in a mainstream school with no interaction with other children without SEND. However, although many children still attend segregated provision, Ukraine is now moving towards an inclusive approach where children with SEND are given the opportunity to attend mainstream schools. This means that many children with SEND now attend standard classes with their peers. Specialist centres conduct assessments of SEND and decide upon the most appropriate form of education for the child in consultation with the parents. Additional support is provided as needed, eg through the provision of Teaching Assistants.
In both Afghanistan and Ukraine SEND can be a sensitive subject for parents with some feeling a sense of stigma or shame around having a child with SEND. Therefore, it is important to be mindful of this possibility when discussing the subject of SEND with parents.
Relationship and Sex Education (RSE)
In Afghanistan children do not learn about sex and relationships at school. In Year 10, pupils may learn about anatomy and how babies are conceived as part of the Biology curriculum but this input excludes girls who do not attend secondary school. They learn about periods at home from their mothers, older sisters or friends and the quality of information is variable. Families may respond differently when informed about the RSE element of the school curriculum in the UK. Some may be happy for their children to receive well-informed advice at school whereas others are more reticent and may prefer to withdraw their children, especially in relation to the theme of same-sex relationships which are not permitted in Afghanistan. It is recommended that settings clarify the content of the RSE sessions and highlight themes such as healthy relationships with parents so they can make an informed decision based on the facts.
In Ukraine, subjects such as Health Education and Biology cover parts of sex education however relationships is not an area that is explored in detail and schools may not provide consistent guidance. Some families may not be comfortable discussing sex education with their children while others may try to do so using books and other resources.
Family and home life
Family is very important in both Ukraine and Afghanistan and it is common for children to live with their extended family, particularly their grandparents. They play a big part in the children’s lives. In fact, grandparents help so much at home that it has been noticed by UK Early Years settings that Ukrainian children can be less independent than their peers with routine tasks such as getting dressed or putting their shoes on. At the same time, it is also usual for Ukrainian parents to leave their young children alone at home to go to work and it can come as a surprise to them that in the UK parents are not expected to do this until children are much older. Similarly young children in Ukraine would usually go to the park or walk to school on their own hence it is useful for settings to be mindful and have conversations about this early on.
Families are also very close in Afghanistan. It is common for several families to live under the same roof and under the responsibility of the grandfather who is the decision-maker. Women are responsible for cleaning, cooking, and taking care of all the children. It’s not unusual for aunts and uncles to raise their nieces and nephews as their own children, which may explain why schools may welcome more than one ‘sibling’ within the same year group. To colleagues in the UK children may not strictly fall under our notion of brother or sister but for the children themselves the relationship is very strong indeed. Questions around children’s dates of birth should be asked sensitively and we must be reminded that not all will know their birth dates anyway.
For Afghan families who practise Islam the routine of the home revolves around prayer. Some families (Sunni Muslims in particular) pray 5 times a day while others (Shia Muslims) may pray 3 times a day. They wake up early for morning prayer. There is another prayer late in the evening after which families will have their dinner hence it is not unusual for children to go to bed late at around 23.00. In Ukraine, parents finish work at 18.00-19.00 to collect their children. Life starts then – families may go out and meet with friends. Children will also tend to go to bed late. Families moving to the UK from both Ukraine and Afghanistan have had to adjust to different routines and synchronise their body clocks to that of UK children who usually go to bed earlier and get up earlier too.
Food and diet is another area that families and children from Ukraine and Afghanistan have struggled with since moving to the UK. At the time of writing many families from Afghanistan are still housed in bridging hotels where they are unable to cook their own meals from fresh ingredients or at times of their choosing. Schools have also commented that many children are hungry during the day because they do not like school dinners. Instead they may bring in hard-boiled eggs and bread from the hotel breakfast buffet which is not always enough to sustain them until the end of a busy school day. In Ukraine, families will typically have a big breakfast consisting of waffles, omelettes, fruit, etc. and will usually have a late lunch consisting usually of soup followed by a main meal. Chips, pizzas and sandwiches and other foods offered at school are not considered a proper lunch.
To conclude this section on family life it is important to note that many refugee families coming to the UK have had to leave family members behind. For example, most Ukrainian children have moved here without their fathers and older brothers because they are required to fight for their country (there are some exceptions). Many Afghan children have also left members of their extended family behind and this can cause a lot of anxiety to those who are unsure about the safety of their loved ones. Families, including mothers who have moved to the UK with their children on their own, are having to cope without their usual support network. We must be reminded that for them juggling everything unaided for the first time can be stressful, particularly in a new country where systems, customs, education and much more are so unfamiliar.
Important dates
School settings should note important religious dates for which families may wish to withdraw their children (they have the right to 1 day for each festival). Schools may wish to take an interest and celebrate these dates through cards, assemblies, etc.
Afghanistan:
Independence day: 19th August
New Year’s day in Persian calendar: 21st March
Eid al-Adha: June 29th 2023
Ramadan: will start around March 23rd 2023 and last approximately 30 days
Eid al-Fitr: end of Ramadan, April 21st 2023
Further dates: Afghanistan Public Holidays 2023 - qppstudio.net
Ukraine:
7th January – Orthodox Christmas
Easter
Birthdays and name days
First Communion
Further dates: Upcoming Ukraine Public Holidays - qppstudio.net
Summing up - recommendations
Find out as much as you can about the background experiences of your new arrivals eg previous experience of school if any, literacy levels in home language(s), etc.
Use Google maps to find out where the children lived before moving to the UK. Did they live in a city or a rural area? Consider how this might have impacted access to services, education and other infrastructures. Consider also how this may have impacted their life experiences eg Afghan children will not be familiar with coasts and may for example need support to access stories and language relating to going to the beach and playing with a bucket and spade
Be aware that some Ukrainian parents may not be comfortable conversing in Russian, particularly to a person who is Russian rather than Ukrainian, even though they may be very competent in speaking Russian as a second language. Bear this in mind when planning to use an interpreter for meetings with parents – if a Ukrainian speaking interpreter is not available and you are considering using a Russian speaker instead always check with the family how they feel about using a Russian speaker before proceeding
Set up a home-school communication book to share details of topics covered at school. This helps families become aware of what their children are learning and is also an opportunity for them to discuss their learning at home in first language
Use ICTs to support communication with parents eg Google Translate, Microsoft Translator, DeepL Translate, SayHi, etc. Note some apps have audio features for some languages and not for others so check this in advance. For example, SayHi recognises speech in Ukrainian and Farsi but not in Pashto and Dari (these require the user to input text using an appropriate keyboard). When talking to parents also give a note written in English so they can get help from others to understand any key messages
Focus on pastoral care and support settling in initially
Discuss routines including bedtime
Clarify expectations regarding behaviour, attendance and punctuality
Explain what children should be able to do by themselves depending on their age eg getting dressed and what they should still be supported with eg walking to school
Be open-minded about children’s wider conception of what close family means
Provide ELSA and bereavement support where appropriate. Use interpreters where required
Talk to pupils about how they would like to observe their faith at school. Offer a space to pray
Provide Muslim children with a vegetarian or fish option. Ensure families understand that these meals are appropriate options for their children
Find out about children’s interests, skills and talents they may have developed in their country of origin eg art, sport, music, cooking, etc.
Clarify content of Relationship and Sex Education sessions
Be mindful that for some parents the subject of SEND can be sensitive
Attend training on how to best cater for the needs of refugee arrivals (see Hampshire EMTAS network meetings) https://www.hants.gov.uk/educationandlearning/emtas/training
Further reading and resources
Coming soon: more information about children speaking Pashto, Dari and Ukrainian will be added to our collection.
Many thanks to Olha Herhel, Kubra Behrooz and Sayed Kazimi for supporting the creation of this blog.
Comments
By Lynne Chinnery
In this three-part autobiographical blog, Hampshire EMTAS Specialist Teacher Advisor Lynne Chinnery takes us on a journey to Libya where she reminisces about the challenges and opportunities of moving to a country so drastically different to her own. In Part 1 and Part 2 we experienced Lynne's culture shock when she first arrived in Libya and read how she eventually found her place. In this final chapter Lynne focusses on her children and the decisions she had to make for the best of her family.
Part 3: Our children
We had made a conscious decision to bring our three children up bilingually from the very beginning as we could see the amazing benefits bilingualism could bring them. And so I mostly spoke to Sami, Leyla and Idris in English and my husband spoke to them in Arabic. As they spent more time with me when they were little, my husband would insist that they spoke to him in Arabic to ensure that they progressed in this language as much as in English. He did this in a playful way, pretending that he didn’t understand them whenever they spoke to him in English and they found this very funny as they knew that his English was really very good. They would use either language when talking to each other, often switching depending on who they were with, but there were some words that, as a family, we always tended to use only in one language or the other because they felt so much better in that language. For example, we’ve always referred to flip-flops or slippers as “shib-shib”, and shout “khalas” when we want someone to stop something. I’ve noticed many bilingual families do the same. Gaining Arabic literacy skills was not a problem, as all their lessons were in Arabic, and it was exciting but a bit daunting for me to see their writing in their school books in a language that I could barely read. I started teaching our children to read and write in English too as there was little of this taught at their schools. It took a lot of time and effort and I can understand why some parents baulk at the task, especially after a long day at work or school.
The Libyan people were warm and welcoming, many of my students became close friends, and I soon found that I regularly bumped into people in the city centre who I knew or who knew me through our school. I also found that the more my Arabic evolved, the happier I was, as I could ask for things in shops, joke with my neighbours and chat to the people in the doctor’s waiting room or on the bus. My children really helped with my Arabic acquisition as I could listen to them speaking Arabic to each other, and they also interpreted for me when I was stuck. I had made some English-speaking friends as well as my Libyan friends and we would meet on the nearby beach every morning during school holidays, which were wonderfully long. Our children would play and swim together while we chatted and shared food and drinks. It was particularly at times like these that our children seemed complete: running across the sand, climbing rocks and jumping into the clear Mediterranean Sea, code-switching from one language to another – half Libyan, half English but now, for these moments, whole.
Over the fourteen years that I lived in Benghazi, life grew easier. Of course there was some racism, as there is in every country. Some people slowed down in their cars to shout insults at me; some people talked about me rather than to me, thinking I couldn’t understand them; and some people were just hostile because I was a foreigner. But these were few compared to the warmth and generosity of the majority of the community; the friendships they offered assuaged the hurt I felt from any racism I experienced.
Our school flourished and we expanded the number of staff and classrooms. We moved from our small flat into a large, family villa with a surrounding garden that I loved to water at night. Gaddafi eased up on his restrictions on private shops and imports and so a much wider choice of groceries and products became available. Satellites arrived and although the government attempted to outlaw them, they were unsuccessful in doing so; the satellite dishes were being raised as fast as they could dismantle them. Eventually, they gave up and we could watch channels from many other countries, mostly Arab countries like Lebanon and Egypt, which had TV programmes and films in both English and Arabic. We were also finally able to watch world news via CNN and Al Jazeera, giving us a less censored version of current events. My husband and our children were happy watching TV in both languages, but I still craved English programmes as a way of switching off and relaxing in an Arabic world.
As time went on, however, it was actually the education in Libya that caused us the most trouble. By the time we had three children of school age, we found ourselves constantly trying to protect them from being beaten in school. We put them into private schools, which at least gave us the right to complain, but the system was still very old-fashioned: the classes were led by strict teachers who stood at their blackboards and dictated what should be copied down or memorised without any discussion. The pupils were sat in formal rows and if they stepped out of line or even answered incorrectly, a short piece of hose pipe or stick was used to hit them on their hands, and in extreme cases on their feet. I can still remember the fear we felt sending our children into such an environment; as well as the dread I felt when my husband was away and I had to go to the school unaccompanied, often to complain to the head about the corporal punishment being used. This would have been a difficult conversation to have in my first language, let alone in one I was still learning. In fact, I found it very stressful to attend any important meetings without someone there with me, even when my Arabic improved.
Eventually, as the political situation was not improving much and because of our growing concern about our children’s education, we decided that we would move back to the UK and put our children in English schools. The plan was that I would move first with the children and that we would visit Benghazi regularly, while my husband stayed on in Libya until he could get a job with a European airline. I had longed for this moment when I had first started living in Libya, but for a long time since, I had become accustomed to my life there: to our school, our home, our family and friends, my students (many of whom had become friends), and so I had stopped wishing that we could move to England. Now, although a part of me felt excited at the thought of moving back to the UK, another part of me felt that I had been away too long.
On my last trip to England, after a period of nearly four years without visiting, I had felt like a foreigner in the UK. It was a terrible realisation when it happened. I had thought that I still didn’t truly belong in Libya, but then upon visiting the UK, I realised to my horror that I didn’t belong there either. So much had happened while I was away, and this took me by surprise because in my head everything had stayed the same. Of course it would change, everything changes, but we don’t think of this when we are away, just as we don’t think about a child growing up and then we are surprised when we see that they are taller and older than before. But it wasn’t only this - I had changed. And so I suddenly had this awful realisation that I no longer belonged anywhere. I have spoken to other immigrants who have been through the same thing: that longing for home, then finding it so different once there that it no longer felt like home. It is a terrible feeling and one I will never forget. Feeling homeless. It does ease with time, and as I returned to Libya after that visit and continued my life there, I just felt that it was Libya which was becoming home to me more and more and I began to realise that I could see things differently to other people, neither one ‘side’ nor the other, a kind of insight into two worlds that are usually seen as poles apart.
So now, given the opportunity to move back to the UK, possibly for good, the thought of returning to live there was both exciting and frightening. Libya, in comparison, seemed safe – it was what I knew. I thought about it long and hard and decided it was right for us at that time and so we came. My husband visited us several times and we visited Libya too, but eventually he met someone else and we split up. I ensured that our children still kept in regular contact with him and they visited Libya at least once a year in the school holidays throughout their childhood.
Although the break-up of our family was a terrible time for all of us, I have never regretted my move back to the UK, especially in light of the terrible turmoil that has ensued there, just as I have never regretted my decision to move to Libya all those years ago. I learnt so much in Libya: the people taught me to understand other ways of living, of seeing, of understanding the world but they also revealed the similarities we all share: the love of family and friends and the hope for peace and security in our lives. They helped me to truly understand that people are people wherever you go and the majority of them are good.
Many thanks to Lynne Chinnery for sharing her personal story. Resources
for parents can be accessed from our website and on our Moodle.
Parents/carers who speak English as an Additional Language | Hampshire County Council (hants.gov.uk)
Advice for parents and carers (hants.gov.uk)
Comments
By Lynne Chinnery
In this three-part autobiographical blog, Hampshire EMTAS Specialist Teacher Advisor, Lynne Chinnery, takes us on a journey to Libya where she reminisces about the challenges and opportunities of moving to a country so drastically different to her own. In Part 1 Lynne sets the scene and readers experience the culture shock she felt when she first arrived in Libya. In this second part we find out how she eventually found her place.

Sami, Leyla and Idris all dressed up for Eid
Part 2: Embracing the culture
After a year, I was pregnant with our first child, Sami, and as my husband didn’t want to leave, I felt I had no choice but to stay. I’m so glad I did.
Life soon settled into a fairly comfortable routine, with the main meal at lunchtime and a siesta afterwards if needed. Work and school were usually mornings only, six days a week but many people had two or more jobs to make ends meet. In the evenings, people stayed up late to make the most of the cooler night air. We sometimes went out to the lake for a walk in the gardens or stayed in and watched television. There were just two channels on Gaddafi’s strictly controlled TV in those days: one in Arabic and the other divided between French and English, mainly so that Gaddafi could spread the word of his Green Book and Socialist Jamahiriya theory. Most programmes were centred on his teachings and his take on the news, but there were some South American soap operas dubbed in Arabic that everyone crowded round to watch, as well as some ancient British sitcoms on the French/English channel for me. Tuning in to watch Terry and June whilst sat in a villa in the heart of Benghazi was a surreal experience, and I was surprised to find myself looking forward to each episode as there was little else I could understand, apart from rented videos and the BBC World Service on the radio.
Politically, Libya was a dictatorship under the complete control of Gaddafi, who was abhorred by the majority of its citizens (or at least that’s how I perceived it in Benghazi, where the resistance to the regime was strongest). But he had been in power so long and his rule was so harsh, that the majority of the population had learnt to live in a state of reluctant acceptance. For many, this was all they had known. Even my husband had been a child of just seven years when Gaddafi first took power from King Idris in a coup in 1969.
With my usual ability to pick the right time, the West had declared sanctions with Libya shortly after I arrived. Private enterprise had been slashed previously under Gaddafi’s vision of a Socialist state and, apart from a few shops selling cloth, which were still allowed to open in Soog AlJareed (a traditional market in the centre of Benghazi), the majority of shopping was done in the large government department stores or in the government Jamias. The department stores stood mostly empty but with one or two products in abundance, such as rows and rows of washing powder, endless lines of canned ghee, or shelves with just one type of skirt or sandals but very little else. The Jamias were local stores where we could buy necessities such as rice, oil and pasta - very important to a country with Italian heritage (Libya had been occupied by Italy from 1911 to 1943 and had retained some of its dishes, language and buildings). All items were modestly priced in the Jamia but rationed and you had to show your ration book in order to acquire them. Occasionally, we could also purchase some electrical goods such as a TV or a washing machine. If there weren’t enough for everybody, a lottery was held (although you still had to pay for the appliance if you won). Anything else people needed was bought on the black market, mostly from suitcase importers who travelled abroad to bring back what they could to sell. Not surprisingly, prices kept rising and the Libyan Dinar fell even further due to the sanctions, meaning that the cost of travelling abroad was particularly high and so I couldn’t visit home as often as planned.
I had been warned not to speak to anyone I didn’t know well about anything political – you could be locked up or even worse, and never to mention politics on the phone or in my letters home as these were all monitored. But with trusted family, friends and colleagues, we could speak freely and a closeness laced with black humour prevailed.
Sometimes there were flurries of physical resistance and I remember once stopping on the great bridge that spanned the largest of the lakes in central Benghazi, watching mortar bombs being fired into a block of flats. It sounds strange now, but we just stood there watching the whole scenario unfold before us as if we were watching a film. The residents had been evacuated because there were insurgents (the side we wanted to win) hiding within. I don’t think we ever found out what happened to them as such events were never reported in the news.
But on the whole, these were exceptions to our everyday life of family, school and work, interspersed with occasional picnics in the nearby countryside, trips to Jabal Al-Akthar Mountains (The Green Mountains) or days spent at one of the many breathtaking beaches. We now had three children: Sami, Leyla and Idris and so our thoughts were mostly preoccupied with acquiring the things we needed on the black market, getting our children ready for school on time, the successful growth of our language school and, for me, trying with great difficulty, to help my children with their Arabic homework and decipher the letters that came through the door when my husband was away.
There were some cultural aspects that I found more difficult to adjust to than others. For example, I just couldn’t understand why women and men had to sit in separate rooms unless they were family or close friends. This was especially painful at the beginning when I didn’t speak Arabic because if I was separated from my husband, I had no one to interpret for me. I also had to learn how short was too short for a skirt or dress, that trousers could only be worn with something long over the top, and that sleeveless tops were shameful. Libya had a real mix of orthodoxy at that time. Although the hijab was rarely worn, you could see women completely covered in a long-sleeved dress down to their ankles and a headscarf hiding their hair or, at the other extreme, you might see a young girl dressed in Western clothes driving by in her sportscar, her hair flying in the wind. Luckily for me, my husband’s family were somewhere in the middle, they were Muslim and believed in modest dress but were not insistent that anyone should wear a scarf, feeling that this was a personal choice.
The longer I stayed in Libya, the more ordinary the customs became to me. As my Arabic grew, I looked forward to the women’s get-togethers, known as ‘lemmas’, as a time to catch up with each other’s news and above all to laugh. I began to feel shy wearing my swimming costume on the beach and started wearing shorts over it as some of the Libyan women did and I wore a long shirt over my trousers when I went out. At home, I often wore a jalabiya: a long shift that was much cooler than jeans and a T-shirt. And I found that sitting on the floor to eat from shared bowls on a low table or tray was actually very sociable and relaxing, plus it certainly saved on the washing up! And all the time I was adjusting, my spoken Arabic was improving as I absorbed it from those around me. My literacy skills were also slowly coming along as I continued to teach myself from a book I had brought with me, and practised reading my children’s school books, frantically trying to keep up with them, but failing.
How did Lynne's family adjust to living in two languages? Come back next week to read the third and final part of her autobiographical blog.
Comments
By Lynne Chinnery
In this three-part autobiographical blog, Hampshire EMTAS Specialist Teacher Advisor, Lynne Chinnery, takes us on a journey to Libya where she reminisces about the challenges and opportunities of moving to a country so drastically different to her own. Readers will reflect and empathise with the experiences of parents of international EAL arrivals settling in the UK.

View across the central lake of Benghazi, prior to the 2011 civil war
Part 1: The Culture Shock
Learning to live in a new country is never easy. The greater the differences that exist between the new language and culture and your own, the tougher it is. I only truly learnt this when I experienced it myself - by moving to Libya.
I had met my husband in Athens and we’d been together as much as possible for three years, during which time I was living in Greece, Turkey and London before moving to his home country of Libya. He was an airline pilot and I had trained as a primary school teacher, but most of my actual working experience had been in TEFL (Teaching English as a Foreign Language). After moving to Libya, I taught privately for a while before we jointly opened a language school on the northern coast of Libya, in his birthplace and our home, Benghazi.
When I first went to Libya, the dramatic change in culture, language, religious views, work, leisure, everything in fact, took me completely by surprise. Of course, I had known it would be different as I had lived abroad before, and it was the difference itself which I usually found so exciting and that inspired me to travel. But this was unlike anything I had ever experienced before; I had so much to learn that I felt bewildered and almost childlike. Part of the problem was my lack of Arabic and the fact that English was far less prevalent than in other countries I had visited; in fact, it had been banned in Libyan schools for some years.
With no understanding of Arabic, apart from a smattering of phrases I had taught myself prior to the move, I was still unable to do little more than greet people and say thank you and goodbye. I had learnt part of the alphabet, which meant I could pick out some letters on the otherwise unintelligible street signs, although even that was difficult as the fonts varied enormously and did not seem to look at all like the letters in my book. I fully understood for the first time how people who do not use the Latin script feel when they first travel to the UK: there was nothing familiar to hold onto.
As I descended from the air-conditioned plane, I was met with that blast of hot air which heat-seeking holiday makers are familiar with, and looking around me, everything was dry and flat, with only distant palm trees breaking up the landscape. As we drove from the airport to the city of Benghazi, however, following the sprawl of the city to its source, the dusty roads were gradually replaced with tarmac and I saw tall apartment blocks with splashes of colour from balconies full of potted plants, hanging rugs and washing. These in turn were soon replaced with villas, their lush gardens overflowing with palms, jasmine and bougainvillaea.
Benghazi had that chaotic mix of many towns and cities, where buildings have sprung up without any plan, a few even adopting part of the street as an extension of their garden. Small, modest houses, some in need of repair, shared the street with gigantic, newly-built villas, most sitting on untarmacked dusty roads that led away from the wide tarmacked road we were driving along. We passed parks with beautiful trees full of red blossoms and cherished, thick grass; interspersed with neglected areas of wasteland that had been left barren, with only dusty palms surviving in the ruddy, sandy soil. As we neared the city centre, modern municipal buildings interrupted more traditional houses and the streets were in the old Italian-style, dotted with shady plazas. At the heart of the city, a beautiful cathedral filled the skyline and the huge central lake of Benghazi stretched out before us. It really was stunning.
Of course, everybody had thought I was crazy to move to Libya, but I was in love with my husband and he talked about Libya in a way that was so different to its portrayal in the media that I had already begun to see it through his eyes. The reality was a shock for me: this time rather than working as an English teacher and living with English-speaking colleagues, I was immersed completely in the new culture. I had to deal with life in a shared house with my new mother-in-law and one of my sisters-in-law, neither of whom spoke English and I found this particularly stressful when my husband was away. Luckily, my other sister-in-law was a doctor and so was fluent in English. When you can’t express yourself in your first language, the relief you feel when someone comes into a room and chats with you in your mother tongue is incredible.
We lived in a beautiful old villa that had been left empty for some time, situated in an area close to the city centre. It belonged to a relative of my husband who had kindly loaned it to our family to use until our apartment was ready. Wide and spacious, with large airy rooms and a garden and veranda encircling it, the charm of our temporary home helped to make up for the fact that all washing water needed to be collected from the garden and drinking water drawn from a well on the outskirts of the city.
Other
differences I needed to get used to were not having a job to occupy me, the
shortage of available goods, a new and very different language to learn and on
top of all this, a multitude of baffling customs to contend with. I felt
overwhelmed, with nothing tangible or familiar to help me. I did think of
leaving; I nearly did leave. But I knew enough to realise that I was suffering
from culture shock more than anything else and agreed to try it for a year.
What will Lynne decide after spending a year in Libya? Come back next week to read Part 2.
Comments
By the Hampshire EMTAS Specialist Teacher Advisors
Welcome to this new academic year. In this blog you will find out what’s in store for 2022-23, starting with a staffing update and news of fantastic heritage language GCSE results. We also share ideas and resources to celebrate World Fun Fair Month and details of upcoming training opportunities. Finally, we have news of our continued support for refugee arrivals and celebrate the achievement of schools on their EAL Excellence Award.
Staffing
To kick off, we have some news about our staffing. We are delighted to welcome new Bilingual Assistants this year, Olha Herel (Ukrainian), Jenny Lau (Cantonese) and Kubra Behrooz (Dari).
From our Teacher Team, last term we bade farewell to Specialist Teacher Advisor Jamie Earnshaw, who worked with schools in Eastleigh, Fareham and Gosport. In his place, Lynne Chinnery is now covering Fareham and Gosport districts in addition to Havant & Waterlooville and the Isle of Wight. As a temporary measure whilst we wait for our new recruit to join the EMTAS Teacher team, Claire Barker is back on the team and covering Eastleigh and East Hants whilst Kate Grant has added Hart to her brief. Helen Smith is covering Rushmoor and all things GTRSB – that’s Gypsy, Traveller, Roma, Showmen and Boater in case you are wondering about the new nomenclature there, following the lead of the Traveller Movement and ‘The Pledge’.
Finally, Michelle Nye, the erstwhile Team Leader, left EMTAS at the start of this term to take up the role of Executive Head of the Virtual School for Hampshire and the Isle of Wight. In her place, Sarah Coles is currently acting Head of Service with Claire Barker as her trusty sidekick, acting up into the Deputy Team Leader role.
GCSE results
2021-22 was a bumper year for Heritage Language GCSEs. In the summer 2022 exam series, EMTAS Bilingual Assistants supported 106 students in schools across the county with their Heritage Language exams. Students took GCSEs in 11 different languages, with Persian added to the list thanks to Sayed Kazimi, our Pashto, Dari and Farsi-speaking Bilingual Assistant who supported our first ever Persian candidate. Our Admin team gathered in the results from schools as soon as we started back in September; the full list is now on the EMTAS website, but we are thrilled to be able to report that 60 of those students achieved Grade 9, with another 25 being awarded Grade 8. Our congratulations go to all those students.
World Fun Fair Month
September is dedicated to celebrating our Showmen children and families. World Fun Fair Month was started by Future 4 Fairgrounds which is a community organisation set up by 6 Showmen women to celebrate the Showmen community as well as raise awareness of the challenges they face. Our team is proud to have supported WFFM by collating ideas and resources for schools to use throughout September to celebrate this important month for our Showmen families. There is still time to share children’s work with us so we can display it on the EMTAS website and Moodle. You can share anything from your school’s celebrations by sending it via email to EMTAS@hants.gov.uk with ‘World Fun Fair Month 2022’ in the subject line, ensuring it includes no photos or names of children (only the names of the schools the children attend will be published).
For your diaries - upcoming training opportunities
Back by popular demand this term are our online network meetings which will be co-delivered after school by different members of the EMTAS Teacher Team. There are three dates for a session focussing on catering for the needs of refugee arrivals: September 22nd, October 11th and November 8th. We also have three dates for a session focussing on the needs of new to English arrivals on September 27th, October 20th and November 16th. There are details of how to join these meetings on our website.
This half-term we also recruit for our Supporting English as an Additional Language (SEAL) course. This course is suitable for teachers, EAL co-ordinators and support staff in both primary and secondary phases. This is a two-year course: it comprises of six units taught over 6 days. It is held in Winchester and starts in November 2022 and ends in May 2024 therefore it can be budgeted over three academic years. The benefits of sending a member of staff on this course are far-reaching. Not only does it upskill a member of your staff in becoming an expert in English as an Additional Language (EAL) but it also leads to raising EAL standards at your school. Through the course colleagues will explore different cultural practices, learn how to confidently assess pupils with EAL including whether a child’s needs are SEN or EAL, discover the latest technologies to help support pupils with EAL and become more aware of how to support parents of children with EAL. The course also helps towards gaining the EAL Excellence Award. For more information about SEAL, please visit our website.
Plans are already underway for our not to be missed EMTAS conference which will take place in the Autumn of 2023. Keep an eye out for save the date information which will be sent out this Spring term. We look forward to seeing many of our blog readers at this event which promises to be as thought-provoking as ever.
Refugee arrivals
EMTAS referrals for refugee pupils are continuing to arrive and we are pleased to see many school colleagues book on our network meetings to find out more about how to cater for this group of children and young people. We are also delighted to see schools make good use of our resources centre by borrowing dual language stories, translated texts and devices such as talking pens.
Some schools in Hampshire and on the Isle of Wight have been
receiving requests from Ukrainian parents for patterns of attendance/provision
that differ from full time attendance at school/participation in mainstream
lessons every day. In many cases families are looking to return to Ukraine once
it is safe to do so and it is therefore understandable that they may want their
child(ren) not to miss out on the Ukrainian curriculum. In a recent School
Communication also available on our Moodle we share some considerations and
points to bear in mind which may help with the decision-making around such
requests as well as alternatives to explore.
Later this term we look forward to adding a new blog to our refugee series where we will unpick the differences and similarities between refugees arriving from Afghanistan and those arriving from Ukraine. Later this academic year we will also be sharing cultural information about these countries on our website.
EXA news
In our previous blog we celebrated the achievement of schools on their GRT and EAL Excellence Awards. As we begin this new academic year, we congratulate even more schools on achieving their EAL Award. A huge well done to Endeavour Primary, Shakespeare Infants, Chalk Ridge Primary and St Matthew's CE Primary School for all their hard work and dedication in improving their practice and provision for their learners with EAL.
Those of you who are currently on your journey to achieve an EXA award may have noticed some changes to the criteria we use to validate. We hope this will further improve standards and that you find it more user friendly. Any schools currently in the process are invited to submit their evidence using either the old, new or a mixture of criteria. As always, if you have any questions regarding the EXA award, please don’t hesitate to get in contact with your Specialist Teacher Advisor.
Heritage Honours Award
Would you like to encourage your learners from BME, EAL and GTRSB backgrounds and reward them for their hard work and perseverance? The Heritage Honours Award was created to celebrate the achievements of these learners and is open to all Hampshire and Isle of Wight schools. Learning a new culture and/or English as an additional language can be a long and difficult path so why not recognise this by nominating them for a Heritage Honours Award? Relevant areas of success could include exceptional progress in acquiring EAL, overcoming adversity, first language achievements eg use of first language as a tool for learning, active involvement in the EMTAS first language pupil training program, storytelling, writing in L1, Heritage Language GCSEs, etc. and promoting linguistic, religious and cultural awareness in school. For more information and details of how to nominate please go to the Heritage Honours section on our Moodle.
Finally...
We are all looking forward to continuing working with you and to sharing more blogs written by different members of our fabulous team. Come back next week to read Lynne Chinnery's Memoirs of a Travelling Teacher.
Comments
By the Hampshire EMTAS Specialist Teacher Advisors
1077 pupils, 60 languages, 70 countries of origin; 2021-22 has been a year like no other. In this blog, we reflect on the highlights of a very busy academic year and share some of the things schools can look forward to after the summer. Notably we discuss our response to our refugee arrivals and Unaccompanied Asylum-Seeking Children, review our SEND work, examine how our research projects are progressing, feedback on our GTRSB work, give an update of developments around the Young Interpreter Scheme, ECT programme and Persona Dolls and celebrate the end of support for Heritage Language GCSEs for this academic year. EMTAS Team Leader Michelle Nye concludes this blog with congratulations, farewells and an update around staffing.
Response to refugee arrivals
As we post this blog, 275 refugee arrivals have been referred to Hampshire EMTAS in 2021-22. These pupils predominantly arrived from Afghanistan and Ukraine with a small number coming from other countries such as El Salvador, Pakistan and Syria. EMTAS welcomed new Bilingual Assistant colleagues to support pupils speaking Ukrainian, Dari/Farsi and Pashto and a lot of work went into supporting and upskilling practitioners in catering for the needs of new refugee arrivals. We delivered a series of online network meetings where colleagues from across Hampshire joined members of the EMTAS Specialist Teacher Advisor team to find out more about suitable provision. We launched a new area on Moodle to share supporting guidance and resources. We published two blogs – Welcoming refugee children and their families and From Kabul to a school in Basingstoke – Maryam’s story. And we added two new language phonelines to our offer, covering Russian and Pashto/Dari/Farsi.
In the Autumn term you can look forward to further dates for network meetings focussing on how to meet the needs of refugee new arrivals. There will also be sessions where we will explore practice and provision in relation to catering for the needs of pupils who are in the early stages of acquiring English as an Additional Language (EAL). In addition to this, we are planning a blog in which we will interview our new Ukrainian-speaking Bilingual Assistant to share with you the specificities of working with Ukrainian children. The team is also working alongside colleagues from HIAS and HIEP to collate FAQs from queries and observations related to asylum seekers and refugees who have recently arrived into Hampshire.
Unaccompanied Asylum-Seeking Children (UASC)
It’s been a busier than usual year for UASC new arrivals too, with 11 young people being referred to us having made long and dangerous journeys to the UK on their own. They have travelled from countries such as Sudan, Iran, Iraq, Afghanistan and Eritrea and speak a variety of languages including Arabic, Kurdish Sorani, Tigrinya and Pashto. The majority have been placed in schools outside of Hampshire and so have been profiled remotely, but some are now attending Hampshire schools meaning that we have been able to visit them in person. There is lots of advice available for schools receiving UASC onto their school roll on our website. This includes detailed good practice guidance and Welcome to Hampshire (an information guide written for the young people) translated into several key languages with audio versions also available.
SEND work
The SEND phone line run by Lisa Kalim continues to be well used by schools as their initial point of contact with EMTAS when they have concerns about a pupil with EAL and suspect that they may have additional needs. There have been almost 100 calls made on this line to date this academic year. After school tends to be the busiest time so if you can ring earlier, it may be easier to get through first time. It is helpful to have first read the information on our website about steps to take when concerned that a pupil with EAL may also have SEND and to have gathered the information suggested in the sample form for recording concerns before calling. In many cases advice can be given over the phone without the need for a teacher advisor visit to the school. However, for others a visit by one of our Teacher Advisors can be arranged. This year, our Teacher Advisors have been especially busy with this aspect of our work and have completed over 60 visits since September. These have focused on establishing whether individual pupils may have additional needs as well as EAL or not and also on the enhanced profiling of those for whom a school will be submitting a request for assessment for an EHCP.
Ongoing research
It’s been a catch-up sort of year for Sarah Coles, with a delayed start to her data collection due to Covid affecting the normal transition programmes schools have for children due to start in Year R in September. Through the Autumn, Spring and Summer terms, Sarah has made visits to schools to work with the eleven children who are involved in her research. The children are either Polish or Nepali heritage and they were all born in the UK. This means they have not experienced a monolingual start to life, hence Sarah’s interest in them and their language development.
The children have talked about their experiences of living in two languages – although as it turns out they’ve had very little to say about this. Code-switching is very much the norm for them and having skills in two languages at such a young age seems to be nothing remarkable or noteworthy in their eyes. They’ve also done story-telling activities in their home languages and in English, once in the autumn term and again in the summer. This will enable comparisons to be made in terms of their language development as they’ve gone through their first year of full time compulsory schooling in the UK.
Early findings suggest big differences between the two language groups. The Nepali children tend to prefer to respond in English and most have not been confident to use Nepali despite all demonstrating that they understand this language when it’s used to address them. This has been the case whether they are more isolated – the only child who has access to Nepali in their class - or part of a larger group of children in the same class who share Nepali as a home language. In contrast, the Polish children have all been much more confident to speak Polish, responding in that language when it’s used to address them as readily as they use English when spoken to in that language. This has been the case whether they’re more isolated at school or part of a bigger cohort of children.
The field work ends in the summer with final interviews with the children’s parents and teachers. Sarah then has a year to write up her findings, submit her thesis and plan how best to share what she’s learned with colleagues in schools.
Young Interpreter news
This academic year Astrid Dinneen launched the Young Interpreter Champion initiative. Young Interpreter Champions are EAL consultants outside Hampshire who are accredited by Hampshire EMTAS to support schools in their area in running the Young Interpreter Scheme according to its intended ethos. Currently 6 Local Authorities are in our directory with more colleagues enquiring about joining.
Established Young Interpreter Champions met on Teams in the Summer term to find out how the Young Interpreter Scheme is developing in participating Local Authorities and to plan forward for 2022-23. They also heard more about Debra Page’s research on the Young Interpreter Scheme under the supervision of the Centre for Literacy and Multilingualism at the University of Reading and with Hampshire EMTAS as a collaborative partner.
The aim of Debra’s research is to evaluate the scheme’s impact on children’s language use, empathy and cultural awareness by comparing Young Interpreter children and non-interpreter children. Her third and final wave of data collection took place during the Autumn term 2021. This year is dedicated to analysing her data and writing her PhD thesis. Her chapter on empathy and the Young Interpreter Scheme is complete and she will soon write a summary about this in a future Young Interpreters Newsletter. She also looks forward to sharing results of what is found out in terms of intercultural awareness and language use.
GRT update
It has been a very busy year for the GRT team. Firstly, we will be moving towards using the more inclusive term of Gypsy, Travellers, Roma, Showmen and Boaters – GTRSB when referring to our communities.
As usual our two Traveller Support Workers Julie Curtis and Steve Clark have been out and about supporting GTRSB pupils in schools. The feedback they receive from schools and families is very positive. The pupils look forward to their opportunity to talk about how things are going and they value having someone listen to them and help sort out any issues. Our Traveller team lead Helen Smith has been meeting with families, pupils and schools to discuss many issues including attendance, transport, exclusions, elective home education (EHE), relationships and sex education, admissions and attainment.
Helen has been lucky enough to work with some members from Futures4Fairground who have advised us on best practice when including Showmen in our Cultural Awareness Training. Members of the F4F team also attended and contributed to our schools’ network meeting and to our GTRSB practitioners’ cross-border meeting.
The team was busy in June encouraging schools to celebrate GRT History Month. We devised activities and collated resources around the theme of ‘homes and belonging’. Helen attended an event to celebrate GRTHM at The University of Sussex. It was aimed at all professionals involved in working with members from all GTRSB communities in educational settings. It was encouraging to see so many professionals attending. Helen particularly enjoyed watching a performance of Crystal’s Vardo by Friends, Family and Travellers.
Sarah and Helen have been making plans for celebrating World Funfair Month in September. We have already put some ideas together for schools on our website and hope to develop them further with help from our friends at Future4Funfairs.
Looking forward to next year, as well as reviewing our GRT Excellence Award, we will be looking at how best to encourage and support our schools to take the GTRSB pledge for schools - improving access, retention and outcomes in education for Gypsies, Travellers, Roma, Showmen and Boaters. Schools that complete our Excellence Award should then be in a position to sign the pledge and confirm their commitment to improving the education for all their GTRSB families.
Early Career Teachers (ECT) programme
The Initial Teacher/Early Career Teacher programme that Lynne Chinnery is preparing for next academic year is really coming together. After a large proportion of student teachers stated they were still uncertain how to support their EAL learners after completing their training programmes (Foley et al, 2018), the EMTAS team decided to do something about it.
Lynne has collated a set of slides to train student and early career teachers on best practice for EAL learners by breaking down the theory and looking at practical ways to implement it in the classroom. The sessions cover such areas as supporting learners who are new to English; strategies to help students access the curriculum; assessing and tracking the progress of EAL learners; and information on the latest resources/ICTs and where to find them.
The programme has been made as interactive as possible in order to reinforce learning, with training that practices what it preaches. For example, it provides opportunities for group discussions that build on the trainees' previous experiences. The trainees can then try out the strategies they have learnt once they are back in the classroom.
Lynne Chinnery has already used the slides on a SCITT training programme and the feedback from that was both positive and useful. One part the students particularly enjoyed and commented on was being taught a mini lesson in another language so that they were literally placed in the position of a new-to-English learner. This term, Lynne and Sarah Coles have met with an artist who is designing the graphics for the training slides - once again demonstrating a feature of EAL good practice: the importance of visuals to convey a message. The focus in the autumn term will be a reflective journal for student teachers to use alongside the training sessions.
Heritage Language GCSEs
This has been a particularly busy year for us supporting students with the Heritage Language GCSEs. We received 136 requests from 32 schools. We provided support for Arabic, Cantonese, German, Greek, Italian, Mandarin, Polish, Portuguese, Russian and Turkish. For the first time this year, we also supported a student with the Persian GCSE.
The details of the packages of support we will be offering next year will be shared with you in the Autumn term. You can also check our website. Remember to get your referrals in to us in good time!
We wish all students good luck as they await their results! A big thank you to Jamie Earnshaw for leading on this huge area of work. Sadly Jamie is leaving at the end of the Summer term. Claire Barker returns from retirement to take over the co-ordination of Heritage Language GCSEs from September.
Persona doll revamp
Persona Dolls are a brilliant resource which provide a wonderful opportunity to encourage some of our youngest learners to explore similarities and differences between people and communities. They allow children time to explore their own culture and learn about the culture of someone else. The EMTAS team currently have around 20 Persona Dolls, all of which come with their own identity, books and resources from their culture to share and celebrate.
Now some of you may have noticed that our Persona Dolls have been enjoying a little hiatus recently. What you will not have seen is all the work that is currently going on behind the scenes in our effort to revamp them. Within our plans we aim to provide better training for schools so that you as practitioners feel more confident in using them within your classrooms. Kate Grant is also looking at ways to incorporate technology so that you can have easier access to supporting guidance, links to learn more about the doll’s heritage and space to share the experience your school has of working with our Persona Dolls. EMTAS know that our schools recognise the value of this wonderful resource and look forward to seeing the positive impact they will have on their return.
Finally, a conclusion by Team Leader Michelle Nye
The last time EMTAS topped 1000 referrals was 7 years ago so it has been one of the busiest years we have experienced in quite a while. This was due to the exceptional number of refugee referrals and to a spike in Malayalam referrals whose families have come to work in our hospitals. On top of this we had over 120 new arrival referrals from Hong Kong; these children are here as part of the British Hong Kong Nationals Overseas Programme.
EMTAS recruited additional bilingual staff and welcome Sayed Kazimi (Pashto/Dari/Farsi), Tsheten Lama-North (Nepali), Kubra Behrooz (Dari), Tommy Thomas (Malayalam), Jenny Lau (Cantonese) and Olha Herhel (Ukrainian) to the team.
We are delighted that schools have been committed to improving their EAL and GRT practice and provision and have achieved an EMTAS EAL or GRT Excellence Award this year. Congratulations to St Swithun Wells, Bramley CE Primary, St James Primary, Marchwood Infant, New Milton Infant, St John the Baptist (Winchester District), Bentley Primary, St Peters Catholic Primary, Swanmore College, Poulner Junior, Grayshott CofE Primary, The Herne Primary, Wellington Community Primary, Marlborough Infants, John Hanson, Fleet Infants, Fairfields Primary, Swanmore CofE Primary, Brookfield Community School, Fernhill School, New Milton Junior Elvetham Heath and Red Barn Primary.
We say goodbye to Jamie Earnshaw, Specialist Teacher Advisor, who has been with EMTAS since 2012. During his ten-year tenure, his work has included producing the late arrival guidance on our website, developing our Accessing the curriculum through first language: student training programme now available for pupils in both primary and secondary phases, and for leading on our Heritage Language GCSE work. His are big shoes to fill and we will miss him immensely; we wish him every success in his new venture.
Enjoy your summer holiday and see you again in September.
Data correct as of 30.06.2022
Word cloud generated on WordArt.com
Comments
By Hampshire EMTAS Bilingual Assistant Eva Molea
In Diary of an EAL Mum, Eva Molea shares the ups and downs of her experience bringing up her daughter, Alice, in the UK. In this instalment, Eva tries to understand ability grouping in secondary school settings.

Imagine it was July,
and you were sitting in the garden on a sunny afternoon, with your cup of tea
and a lovely book, engrossed in your reading. Everything was great, and you were
looking forward to an idle couple of hours until you had to taxi your child to
their afterschool club. Hold on to this dream as long as you can…
My dream couple of hours vanished as I straightened up on my chair and tried to make sense of what Alice was telling me. It seemed that, from Year 8 onwards, the school would be grouping children according to their abilities, and that some subjects would be bundled together. Therefore, if a child happened to be brilliant in one subject, but not so shiny in the other one, they would be put in the group (= set) of the less shiny subject.
My first reaction was: This is crazy! One of us must have not understood correctly. Check again.
My second reaction was: This is unfair and penalising – with all the self-confidence and self-esteem consequences, especially after the pandemic – whereas the children should be praised for their abilities and efforts.
I tried to think of the information in the school prospectus, of all the things that my friends with older children at the same school had told me, looked at the school policies but could not find an answer, so I decided to write to the school.
I blamed poor Alice because “she certainly had misunderstood what she had been told and it would not be fair to penalise her in Spanish because of her results in Maths”. Spanish and Maths sounded like a strange matching.
Anyway, less than 2 hours later I received a phone call from the Head of Maths (!) who had kindly made time to talk to me about my email. He explained that for the first time, the following academic year, the school would be trying a different type of subject association which saw Maths with MFL, and English with Science. He also explained that to be in the highest set, Alice would have needed high marks at the last tests. Before calling me, he had discussed Alice’s attainment with the Head of MFL, who had confirmed her being an able linguist, which is often the case with bilingual children. Even so, she might have gone down a set because of her attainment in Maths. My understanding was that there were also some timetabling issues involved.
I was very confused. Like many EAL parents, I had been educated in a different system, where children are taught in mixed abilities groups from Year 1 to Year 13, classes are up to 30 children, every child has favourite subjects or is confident in some areas more than in others, and children learn from each other, and from each other’s mistakes as well. Therefore, I was not prepared for this kind of grouping, and wished I had known before, as it would have given us the chance to put in place some support for Alice so that she could feel more confident with her Maths.
I did ask why parents, especially the EAL ones, were not informed about the grouping system and it seemed that nobody had ever raised the issue. So far. The lovely gentlemen said that he would discuss with the SLT how to communicate more clearly with parents.
Needless to say, I was none the wiser after this conversation, because even if I could in part understand the school’s reasons, I still felt that the children were not being treated fairly.
A lot of questions sprang to my mind: would Alice be able to move from one set to the other if her attainment improved? And would she be able to move from one set to another during the academic year or would she need to wait to be in Year 9 to be in the higher set? Would moving up in Maths automatically mean that she would move up in Spanish too? And what if she moved down? And what if she wasn’t appropriately challenged in a lower set?
At this point, my curiosity had been ignited, so I did a little research about different types of grouping in secondary school.
I looked at the EMTAS Position Statement on the placement of EAL learners, which clearly explains that the language barrier might not allow students to demonstrate their full knowledge or abilities and, funnily enough, Maths is the only subject in which Alice still thinks in Italian.
The position statement highlights that EAL learners might understands ideas or concepts in first language, including those which are more abstract and complex, and be confidently able to demonstrate this understanding in their first language. However, when asked to demonstrate this understanding in English, they might lack the necessary language of instruction to fully understand the task they are being asked to complete. Equally, they might not have a sufficient command of English vocabulary or language structures to be able to convey their understanding to school staff or peers.
According to the Position Statement, a thorough EAL assessment would be needed to find out the knowledge and ability of a child in first language and it would be good to discuss any decisions about grouping/setting/streaming with the learner and their parents/carers, who might not be familiar with the UK education system and how decisions on grouping are taken.
I did further research on setting and streaming and the outcome will be part of an new piece of work EMTAS is doing on EAL Parents FAQ.
Fortunately, a few days after my conversation with the Head of Maths, I received an email saying that Alice had done really well in her last Maths test and, therefore, she would be placed in the highest sets in both subjects. I was very pleased for her. She was safe for this year but would have to work very hard in Maths to remain in the highest set. Obviously, I set Dad on a mission to find the best maths revision guides and exercise books, so that Alice could have a little extra practice every now and then, and kindly asked him to patiently instil his love for Maths in our daughter (after all he is an engineer, offspring of a Maths teacher). Patiently being the key word here, I can see a Maths tutor coming our way. ?
Comments
By EMTAS Specialist Teacher Advisor Lynne Chinnery

With an average of one in six pupils in UK schools learning English as an Additional Language (EAL), every student teacher will unquestionably need a solid understanding of EAL pedagogy and how to apply it in the classroom. But how important is EAL these days? You may have noticed a distinct lack of focus on EAL in the OFSTED Inspection Framework but there is at least a mention in the DfE’s Teachers’ Standards. Does this mean that an understanding of EAL good practice is no longer as important for practitioners as it used to be? Is EAL support and training no longer required apart from a cursory nod?
Clearly not, as the number of EAL learners in our schools is increasing, not declining. The Bell Foundation states that, “nearly half of all teachers in England will be teaching pupils from diverse backgrounds, and superdiversity in schools is becoming the norm.” This is no surprise to the Hampshire EMTAS team as our number of EAL referrals and requests for support continues to grow.
In fact, schools sought our support for a total of 30 different languages in March alone! It is therefore rather worrying that EAL is a key area flagged up by both student teachers and newly-qualified teachers as one they feel the least prepared in.
In a study by The Bell Foundation and the University of Edinburgh (Foley et al, 2018), a third of student teachers reported that they had “little” or “little to no” understanding of how to support the language and literacy needs of their EAL learners. And although the majority of trainees understood that teachers had a responsibility for EAL, approximately one half of them said that they had received no EAL input at all during their school placements. It was even found that the teacher trainers themselves lacked confidence in their own knowledge and experience of EAL. This is despite the fact that standard five in the Teachers’ Standards states that teachers must “have a clear understanding of the needs of all pupils … including those with EAL” and “be able to use and evaluate distinctive teaching approaches to engage and support them.”
Furthermore, the National Curriculum Statutory Guidance (2014, Section 4.5) clearly states that teachers must ‘take account of the needs of pupils whose first language is not English’, showing that EAL should be an important component of teacher education programmes. EAL is not a separate subject, but rather a pedagogy that should be considered throughout the curriculum, and needs to be taught as a distinct discipline to ensure its theory, practice and strategies are understood. Students’ training courses can differ greatly from region to region and the opportunities for EAL experience will depend very much on the schools they are placed in and the training provided on their course, all of which seem to be rather hit and miss.
Some areas that were lacking in Initial Teacher Training
(ITT) programmes were identified in the Bell Foundation/Edinburgh University study and
they include:
- understanding the value and use of home
languages in the classroom
- the need for student teachers to expand their
own knowledge about other languages and their differences
- developing understanding of the cognitive and
emotional demands of moving between languages
- learning to apply their EAL theory and
practice across all subjects and levels.
I was particularly surprised that understanding the value of other languages in the classroom was identified as one of the missing areas. It seems to me that promoting the first language is one of the key elements of good EAL practice and the responsibility of every school. Without it, we are ignoring a significant part of an EAL learner’s life and identity, as well as missing out on a valuable resource right there in the classroom. (If you would like ideas and resources to support the use of the first language across the curriculum, see the section Use of First and Other Languages on our Moodle.)
Whatever EAL training is put in place for ITTs, it will need to continue and be built upon as teachers enter their first years of teaching and beyond. The NQT programme was replaced with the Early Careers Framework (ECF) in September 2021 and this phase extended to two years. The Early Career Teachers (ECTs) will have support from a dedicated mentor as well as time off timetable for induction activities and training, in the hope that fewer of them will leave the profession during their induction period. The DfE are also hoping that the ECF will build on the ITT and “become the cornerstone of a successful career in teaching”.
Yet once again, we have a discrepancy between what is expected and what is taught. The new ECF is closely aligned to the Teachers’ Standards, and yet makes no reference to EAL, which means that as long as the training providers stick to the ECT programme, the inclusion of EAL is discretionary. And so it would seem that the EAL training provided in the ECF could be as ad hoc as that in the ITT.
The last annual DfE survey of NQTs (which was pre-Covid) showed that many were concerned about their ability to teach EAL. I doubt much has changed since then. In her article How well prepared to teach EAL learners do teachers feel? Emily Starbuck says that “NQTs have consistently given this aspect of their training the lowest rating.” In fact, most of those questioned reported having had little or no training on their ITT to enable them to meet the needs of EAL learners. They also felt that it would be difficult to improve their practice due to a lack of external guidance; many stating that CPD opportunities and school support in the field of EAL were unavailable. As one teacher in the survey said, “Most of the training was geared towards mainstream.”
The Bell Foundation report clearly states that in order for all teachers to be prepared to meet the needs of EAL learners, Initial Teacher Education should not be seen as a separate component in a teacher’s career but should be viewed as the first step in their continuing professional development. It is therefore important that the groundwork on EAL taught to trainee teachers in the ITT stage is built upon as they progress through their careers.
Why then is EAL not being addressed more in Initial Teacher Training (ITT) programmes and the ECF? Without knowledge of best-practice principles in the field of EAL and guidance on how to apply them, student teachers and early career teachers are more likely to make poor or uninformed decisions when faced with learners who are new to English as well as more advanced EAL learners. Some examples the EMTAS team have seen include the deceleration of students, unnecessary withdrawal from the classroom and the use of inappropriate resources. Inexperienced students and teachers are also more likely to judge a student’s ability from their spoken communication (BICS), and therefore fail to provide enough support with their academic and literacy skills (CALP). (To understand BICS and CALP, watch this: Terms to Know: BICS and CALP.)
Newly-qualified and student teachers will need ideas and strategies that they can use to scaffold the curriculum content for their EAL learners; an hour-long session on ‘the basics’ of EAL is not going to suffice. With this in mind, I have been working with my colleagues at Hampshire EMTAS on an in-depth ITE and ECF training programme to fill this potential void and deliver up-to-date training. Using the pedagogy of EAL to guide the trainees, but with practical ideas for EAL support in the classroom, we hope that our training programme will give the attendees the confidence they need.
We hope that the termly training sessions will run as a steady progression from Initial Teacher Training right through to the end of the Early Career Teacher programme. The training will consist of a set of modules, based on the findings of The Bell Foundation's recent research, but using strategies, resources and ideas from across the Hampshire EMTAS Teacher Team. Each session is designed to be as interactive as possible, with plenty of group activities and discussion, so that the trainees have the opportunity to share their experiences in the classroom and learn from each other. This will have the additional benefit of promoting the value of collaborative work by having the trainees experience it for themselves.
There will be a reflective journal to
accompany the course so that the ITTs and ECTs can review their learning and
thoughts from each session, as well as plan strategies to explore once back in
the classroom. Some of the areas that will be included in the training are:
- understanding the
stages of language development such as the silent period
- ways to include
the EAL learner in the classroom and scaffold their learning
- collaborative work
and setting/grouping
- knowing how to
advise parents on bilingualism/multilingualism
- assessment,
tracking and planning for EAL.
We also ensure that student teachers and ECTs are made aware of appropriate, up-to-date resources and where to find them.
By equipping students and teachers with the knowledge and strategies they need, I hope that they will view EAL in a similar way to Sheila Hopkins: 'multilingualism should be seen as a valuable resource and an integral part of a child’s identity, rather than as a hindrance'.
I will continue to work and build on the training course
and hope to share my progress once I'm done – although as we all know from Kolb’s
Learning Cycle, a teacher’s work, just like a student’s, is never really
“done.”
References
Naldic (2016) EAL Learners in Schools
The Bell Foundation (2018) University of Edinburgh Research Report, English as an Additional Language and Initial Teacher Education
Department for Education (2021) Teachers’ Standards in England
The
Bell Foundation (2019) University of Edinburgh Executive Summary, English as an
Additional Language and Initial Teacher Education
The
Bell Foundation (2020) Designing New ITE Curricula: EAL Content
Recommendations
DfE (2019) Early Career Framework
DfE
(2018) Newly Qualified Teachers: Annual Survey, 2018 Research Report
Hamish
Chalmers (2018) How well prepared to teach EAL learners do teachers feel?
Sheila Hopkins (2022) Supporting trainee teachers to teach EAL pupils
Hampshire EMTAS Guidance Library
Comments
Written by Helen Smith, Lynne Chinnery and Sarah Coles, all of the Hampshire EMTAS Specialist Teacher Advisor team, this blog presents the latest addition to the suite of EMTAS e-learning modules, 'Developing Culturally Inclusive Practice in Early Years Settings'. The new module is aimed at practitioners working in Early Years settings with children and families for whom English is an Additional Language (EAL), or who are from Gypsy, Roma & Traveller (GRT) or Black and Minority Ethnic (BME) backgrounds.

The EYFS Statutory Framework states that “providers have a responsibility to ensure positive attitudes to diversity and difference. Not only so that every child is included and not disadvantaged, but also so that they learn from the earliest age to value diversity in others and grow up making a positive contribution to society”. The themes of inclusion and diversity pinpointed in this statement form the foundation on which the EMTAS Early Years e-learning module sits.
Why Early Years e-learning?
Practitioners in Early Years settings often wonder if what they’re doing for the EAL, GRT and BME children in their care is good practice, as inclusive of the needs of all children and their families as possible. Elsewhere, in settings that don’t have any children from these backgrounds – few and far between these days - work in this area is recognised as equally important. Yet it can be a challenge to find affordable guidance and training to help develop practitioners’ knowledge and understanding of their inclusion brief, without which they may not feel entirely confident when it comes to delivering fully inclusive practice in settings.
There are many questions practitioners might have about their contributions towards the diversity and inclusion agenda. For instance, what advice should they give families whose home language is not English? Should they tell them to carry on speaking their home language(s) to their child or swap to English instead? The answer to this one is that parents/carers should carry on using their strongest language with their child. It really doesn’t matter what that language is; young children can cope with more than one language from an early age and for parents to continue using the home language whilst their child gained exposure to English in an Early Years setting would be one way of raising a child bilingually (there are others). It is also the best way of ensuring that the child develops secure language skills whilst at the same time staying in touch with their cultural and linguistic identity.
For some children, coming into an Early Years setting can bring
many new experiences they have to learn to manage. For GRT children used to an ordered,
uncluttered home environment, the setting might seem chaotic and overwhelming
with its bright colours, numerous toys and messy play. GRT children may have played outside a lot
and may therefore find being indoors sitting still at an activity very
challenging. The e-learning explains
this and other aspects of GRT cultures so that practitioners can grow their
understanding of how best to support GRT children attending their setting.
Other children may come with limited or no experience of being in an English-speaking environment. Accustomed to being spoken to in Urdu or Dari or Polish at home, this can be disconcerting and can result in some children becoming silent in the setting, especially at the beginning – which in turn can be a cause for concern to practitioners and parents alike. The e-learning will help staff better understand things like the ‘silent period’ as well as know what to do to support a child through it.
The term “Black and Minority Ethnic” is more comprehensive and generally encompasses a much broader sweep of children and families, not all of whom will speak another language or have lived in another country. The issues around diversity that staff in settings need to consider in relation to BME children may arise out of language differences, cultural differences, religious differences and/or differences relating to ethnic identity. Images on display in a setting should positively reflect diversity, especially so in settings where the majority population is white. Think also about the books used for story telling; do they include pictures of different kinds of families or of children of different ethnicities? Have you thought about choosing stories that don’t focus on pigs if you work with Muslim families? Or stories that reflect some of the home experiences of your GRT children? If this all seems a bit overwhelming, take heart; the e-learning will help guide you through the diversity maze and empower you to make some carefully considered choices when it comes to provision in your setting.
Towards a more holistic view of the unique child
Cultural and/or language barriers can mask what children are able to do, hiding their interests, skills, abilities and home experiences from staff in settings. Yet it’s really important that practitioners make efforts to find out what children bring with them to the setting. This can help staff better tailor provision so each child receives the best experience from their attendance.
Completing the e-learning will support practitioners to explore and understand what the features of a truly inclusive setting are. This will in turn help them develop their own practice so they give the best start to all their children.
Getting started
Try doing a learning walk around your setting with another member of staff. Ask yourselves if what you see reflects the diversity that exists in the wider world. Do the books you share with children include different languages and images of people from diverse backgrounds? Do you have cooking utensils from other cultural traditions in your home corner? What about the clothing in the dressing-up box?
If you’re not sure where to begin with a learning walk like this, the EMTAS Early Years e-learning can help. It presents guidance and information about a range of issues related to inclusion and diversity using images, short pieces of text and interactive activities like the one shown below.
Screen shot of an interactive activity from the Early Years e-learning module
Included in the module is a checklist practitioners can use to evaluate practice and provision in their setting. It will support you to develop an action plan appropriate to your own children, staff and setting, so any developmental work you undertake will be focused and meaningful, delivering positive change. It also signposts you to further sources of guidance and to resources you might use with children in your setting, many of which are free.
Contact EMTAS to discuss how to gain access to the Early
Years e-learning for staff in your setting.
The price varies according to the number of registrations you need.
Further reading/resources
Free guidance for EYFS from The Bell Foundation:
https://www.bell-foundation.org.uk/app/uploads/2019/01/Guiding-principles-for-EYFS.pdf
Food for thought plus signposting available from Entrust:
Reflecting
on Equality, Diversity and Inclusion in the Early Years | Entrust
(entrust-ed.co.uk)
Suppliers of multicultural books:
Multicultural
Diversity Children's Books - Letterbox Library
Mantra Lingua UK |
Dual language books and bilingual books and resources for bilingual children
and parents and for the multi-lingual classroom.
Free comprehensive guidance pack from Hampshire EMTAS:
Guidance
for Early Years/Year R settings | Hampshire County Council (hants.gov.uk)
Comments
By Chris Pim